Tiny Black Beetles Baby Tiny Black Beetle "White Band on Neck" Florida
ENTFACT-601: Carpet Beetles | Download PDF
past Michael F. Potter, Extension Entomologist
University of Kentucky College of Agriculture
Carpet beetles, equally their proper noun implies, sometimes infest carpets. Similar to dress moths, the pests besides feed on many other items composed of wool, fur, felt, silk, feathers, skins, and leather. Such materials contain keratin, a fibrous beast poly peptide which the larvae are able to assimilate. Cotton and synthetic fabrics such as polyester and rayon are rarely attacked unless composite with wool, or heavily soiled with nutrient stains or body oils. Infestations of carpet beetles can develop undetected, causing harm to vulnerable items.
Facts near Carpet Beetles
Carpeting beetles are common in dwellings, and their damage is often mistaken for that of dress moths.(For more than information about clothes moths, see University of Kentucky Entomology Entfact-609.) The adults are pocket-size (1/16 to ane/8-inch), oval-shaped beetles ranging in color from black- to diverse 'mottled' patterns of white, brown, yellow and orange. Adult carpet beetles feed on flower pollen and do not damage woolens and other fabrics. In springtime, they often appear on windowsills, suggesting an infestation may exist present inside the dwelling. Female beetles lay about 50-100 eggs on or most vulnerable materials. While some convenance sites may exist obvious (due east.g., a wool carpet stored in a cupboard), others can be subtle—for example, accumulations of pet hair associated with baseboards, air vents and ducts.

Fig. ane: Adult carpet beetles are small and often announced speckled or mottled.
In a few weeks, the tiny eggs laid by adult beetles hatch into the fabric-consuming larvae. Larvae are virtually one/8 to 1/4-inch long, tan to brownish in color, slow moving, anddensely covered with hairs or bristles.The developing larvae also leave behind shed (molted) skins. As they graze forth the surface of susceptible materials, they often leave threadbare spots and irregular holes.


Fig. 2: A typical larva (top) and shed pare (bottom).

Fig. 3: Feeding harm caused by carpet beetles.
Every bit noted earlier, carpet beetle larvae feed on beast-based materials, specially wool, felt, fur, silk, feathers and leather. Unremarkably attacked items include sweaters, scarves, coats, blankets, rugs, down pillows and comforters, upholstery, toys, decorative items, and taxidermy mounts. The larvae often feed within fabric folds (hems, collars, cuffs, etc.) in closets, chests and boxes where items are stored for long periods. Clothing and blankets in regular apply are seldom attacked; the same is truthful of rugs that are routinely vacuumed. Edges and undersides of rugs and carpets are more probable to exist infested than areas out in the open.

Fig. 4: Carpet beetles are frequently constitute around the edges of rugs and carpets.
Carpet beetles can also thrive on lint, pilus, and debris accumulating under baseboards and inside floor vents and ducts. The pests can also proliferate on bird nests, animal carcasses, and dead insects (cluster flies, lady beetles, stink bugs, wasps, etc.), which tend to be associated with attics, chimneys, basements, and light fixtures. Dissimilar clothes moths, some varieties of carpet beetle will besides infest seeds, cereals, pet nutrient, and other plant-based materials. Considering of this various diet, the pests may be found well-nigh anywhere in homes, oftentimes making emptying a challenge.
Managing Infestations
Preventing Infestations . As with apparel moths, the all-time way to avert problems with carpet beetles is prevention. Woolens and other susceptible items should exist dry-cleaned or laundered before existence stored for long periods. Cleaning kills any eggs or larvae that may be present, and removes perspiration odors that tend to attract pests. Manufactures to be stored should and then be packed in tight-plumbing equipment plastic bags or containers.
Householders intending to employ moth balls, flakes or crystals should advisedly read and follow label directions. The volatile, odiferous products containing naphthalene or paradichlorobenzene tin be chancy if used incorrectly. Never scatter them in open closets or other areas where children or pets can reach them. The vapors are only effective in deterring textile pests if maintained at sufficient concentrations. Effective concentrations tin can best be accomplished by sealing susceptible items (with the specified dosage of assurance, flakes or crystals) in large plastic bags inside tight-plumbing fixtures trunks, totes, or boxes.
Valuable garments such as furs can too be protected from carpet beetles by storing them in common cold vaults, a service offered by some furriers and department stores. Opposite to pop conventionalities, cedar closets or chests are seldom constructive in deterring cloth pests because the seal is insufficient to maintain lethal or repellent concentrations of the volatile oil of cedar.
Controlling Infestations .To eliminate rug beetles, you lot must locate all infested items. The primary source may be a seldom-used wool or fur lid or scarf on a shelf in a closet; an antique rug stored in the basement; or the remains of a bird or squirrel nest up in the attic. Carpet beetles prefer to dwell in nighttime, undisturbed areas where susceptible items are stored for long periods. When inspecting clothing, pay attention to seams, folds, and creases (e.1000. cuffs and collars) where larvae often prefer to feed. Larvae also tend to infest the lower edges of rugs and carpet. Use needle-nose pliers to lift the outer border of wall-to-wall carpeting from the tack strip along baseboards. Other possible locations include under/within upholstered furniture, or within flooring vents and ducts with accumulations of pet pilus and lint. Every bit noted before, infestations may also stem from bird nests, brute carcasses, or accumulations of expressionless insects such as flies or lady beetles in attics or elsewhere. Plant-based materials (cereal, pet nutrient, bird seed, etc.) stored in kitchens and basements, or cached by rodents, are other possible sources of carpet beetles.
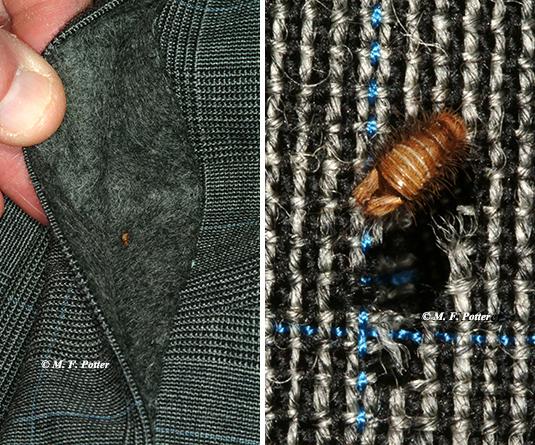

Fig. five: Carpeting beetle larva feeding on a wool sports jacket. Concealed areas (e.thousand., cuffs, collars, cloth folds) are frequently preferred.
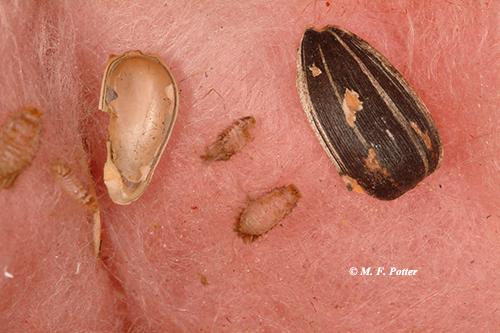
Fig. 6: Shed (molted) skins of carpet beetles associated with mice nesting in an cranium.
Once found, infested items and susceptible articles nearby should be laundered, dry out-cleaned or discarded. Bagging heavily infested items before disposal can help prevent further spread of the beetles. Dry-cleaning or hot laundering kills any eggs or larvae that may exist present. Oestrus generated by a clothes dryer is effective every bit well. Vacuuming floors, carpets, and inside heating vents finer removes larvae likewise equally pilus and lint, which could support future infestations. Exist sure to vacuum forth and beneath edges of carpets, along baseboards, underneath furniture and stored items, and inside closets and tranquillity areas where carpet beetles (and clothes moths) prefer to feed.

Fig. 7: Removing accumulations of lint and hair can help prevent problems with carpeting beetles.
Insecticides applied to infested rugs and carpets may be helpful as a supplement to practiced housekeeping. Sprays recommended for flea control (see Academy of Kentucky Entomology Entfact-602), or with fabric insects listed on the characterization are effective. When treating, pay particular attending to carpet edges, floor/wall junctions, beneath furniture, and bottoms of closets. Infested clothing or bedding should non be treated with insecticides.
Additional Tips for At-Risk Groups
Detecting Infestations . Museums, rug-dealers, craft shops, furriers and taxidermists have much at stake in preventing carpet beetles and clothes moths. Museum collections, in item, can be irreparably harmed by these pests making prevention a necessity. To minimize the run a risk, vulnerable items should be routinely monitored for signs of pest activity. Objects on display and in storage should be closely examined for holes, 'grazed' areas, discrete hair, fur, or feathers, webbing, fecal pellets, larvae, or adult beetles. Since a favored food of the larvae is dead insects, insect collections maintained past museums and hobbyists should be checked regularly for accumulations of 'grit' and debris beneath specimens— a telltale sign that these pests are present. (Tightly sealed collection boxes can be protected from futurity attack past inclusion of moth balls or dichlorvos/DDVP-treated strips.)

Fig. 8: Carpet beetles also scavenge on dead insects (note the shed skins and debris beside the cockroach carcass).
Glue traps provisioned with or without an attractant lure are also useful for detecting infestations. The traps are oft effective at revealing infestations in the early stages when the pests are hard to find by inspection alone. Baited or non-baited traps may exist placed on shelves, inside closets, or wherever susceptible items occur. In large storage or display areas, the devices can be installed in a grid pattern to help pinpoint infested materials, i.e., areas where college numbers of beetles are captured tend to be closer to infested materials.
Traps for monitoring rug beetles (and dress moths) tin can exist purchased online from such suppliers every bit Insects Limited (https://store.insectslimited.com). Since some varieties of fabric pests are attracted to a distinct aroma, it is of import to know which type of beetle or moth you have before ordering.
Thermal Disinfestation. Insecticide sprays are often of limited utilize against carpet beetles, since the pests are often within materials where sprays cannot penetrate. Risk of contagion and staining farther negates their apply on museum objects, wearable, etc. Such items can often be disinfested more finer utilizing a household, chest, or walk-in freezer. In social club to kill carpeting beetles and clothes moths, infested items need to exist held at minimum temperature of 0 degrees Fahrenheit for at to the lowest degree one week. Freezers capable of reaching minus 20 degrees F are able to kill all life stages within 72 hours.

Fig. 9: Freezing is an effective mode to impale carpet beetles and clothes moths.
Before freezing, articles should be placed in plastic numberless, or wrapped in polyethylene sheeting and sealed with tape. This prevents frost and ice from forming on objects during chilling, and condensation later on removal. Later on freezing, objects should be allowed to render to room temperature (for about 24 hours) earlier being unwrapped or further handled. Some items become brittle at low temperatures, and this will help to reduce breakage. For more tips on using cold (and heat) to control pests, see University of Kentucky Entomology Entfact-640, Thermal Disinfestation of Household Items. Another practiced online resources for managing pests in museums and other collection-belongings institutions is http://museumpests.net/.

Fig. 10: Prior to freezing, items (such as this taxidermy mount) should be wrapped in plastic.
CAUTION: Some pesticides mentioned in this publication may not be legal in your expanse of the state. If in dubiety, please consult your local cooperative extension service or regulatory agency. ALWAYS READ AND FOLLOW LABEL DIRECTIONS FOR THE PRODUCT YOU ARE USING.
Please note that content and photos in this publication are copyrighted material and may not be copied or downloaded without permission of the Department of Entomology, Academy of Kentucky.
Source: https://entomology.ca.uky.edu/ef601
0 Response to "Tiny Black Beetles Baby Tiny Black Beetle "White Band on Neck" Florida"
Post a Comment